What do machines dream of? New images released by Google give us one potential answer: hypnotic landscapes of buildings, fountains and bridges merging into one.
The pictures, which veer from beautiful to terrifying, were created by the company’s image recognition neural network, which has been “taught” to identify features such as buildings, animals and objects in photographs.
They were created by feeding a picture into the network, asking it to recognise a feature of it, and modify the picture to emphasise the feature it recognises. That modified picture is then fed back into the network, which is again tasked to recognise features and emphasise them, and so on. Eventually, the feedback loop modifies the picture beyond all recognition.
At a low level, the neural network might be tasked merely to detect the edges on an image. In that case, the picture becomes painterly, an effect that will be instantly familiar to anyone who has experience playing about with photoshop filters:

But if the neural network is tasked with finding a more complex feature – such as animals – in an image, it ends up generating a much more disturbing hallucination:

Ultimately, the software can even run on an image which is nothing more than random noise, generating features that are entirely of its own imagination.

Here’s what happens if you task a network focused on finding building features with finding and enhancing them in a featureless image:

The pictures are stunning, but they’re more than just for show. Neural networks are a common feature of machine learning: rather than explicitly programme a computer so that it knows how to recognise an image, the company feeds it images and lets it piece together the key features itself.
But that can result in software that is rather opaque. It’s difficult to know what features the software is examining, and which it has overlooked. For instance, asking the network to discover dumbbells in a picture of random noise reveals it thinks that a dumbbell has to have a muscular arm gripping it:
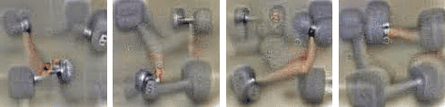
The solution might be to feed it more images of dumbbells sitting on the ground, until it understands that the arm isn’t an intrinsic part of the dumbbell.
“One of the challenges of neural networks is understanding what exactly goes on at each layer. We know that after training, each layer progressively extracts higher and higher-level features of the image, until the final layer essentially makes a decision on what the image shows. For example, the first layer may look for edges or corners. Intermediate layers interpret the basic features to look for overall shapes or components, such as a door or a leaf. The final few layers assemble those into complete interpretations – these neurons activate in response to very complex things such as entire buildings or trees,” explain the Google engineers on the company’s research blog.

“One way to visualise what goes on is to turn the network upside down and ask it to enhance an input image in such a way as to elicit a particular interpretation,” they add. “Say you want to know what sort of image would result in ‘banana’. Start with an image full of random noise, then gradually tweak the image towards what the neural net considers a banana.”
The image recognition software has already made it into consumer products. Google’s new photo service, Google Photos, features the option to search images with text: entering “dog”, for instance, will pull out every image Google can find which has a dog in it (and occasionally images with other quadrupedal mammals, as well).
So there you have it: Androids don’t just dream of electric sheep; they also dream of mesmerising, multicoloured landscapes.

Comments (…)
Sign in or create your Guardian account to join the discussion