Could Beer Power Your Electric Car?

It sounds like a car guy’s fantasy, using beer to power a car.
And it still is fantasy, unfortunately.
However, a couple of researchers at the University of Colorado Boulder have filed for a patent on a method to use the byproduct of the brewing process to create anodes for lithium-ion batteries, the power source for most electric cars.
Currently, no pun intended, the very pure graphite that is used to make lithium-ion batteries is mined, primarily in China, and then doped with other elements like cobalt and magnesium as it is processed into anodes. Engineers Justin Whiteley and Tyler Huggins say their method is more environmentally friendly than mining, more sustainable, and — of greatest importance in commercializing the process — cheaper than extracting it from the earth.
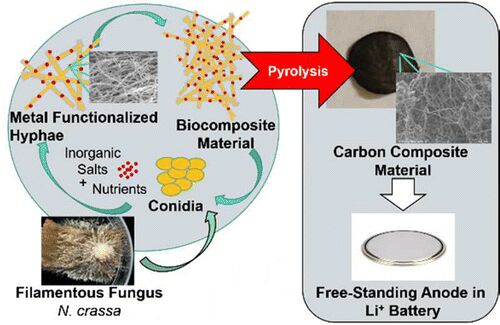
Besides cleaning up the battery building process, the method also promises to make brewing beer more environmentally friendly. It takes about seven barrels of water to make one barrel of beer. That six gallons of wastewater contains sugars and organic materials that have to be rigorously filtered before it can be returned to municipal water systems. Working with Boulder’s Avery Brewing, Huggins and Whiteley used the wastewater to feed the mycelium of a fungus called Neurospora crassa, cultivated on growing media that was rich in cobalt and magnesium. Mycelium is the filamentous vegetative stage of life for fungi between spores and fruit. The fungus effectively filters the water as it consumes the contaminants.
Once grown, the fungus is dried and then baked (actually, pyrolyzed) at 800°C, and the result is a co-doped electrode material that is ready to be used in batteries.
Whiteley told Boulder’s Fox 31, “Out pops this carbon, and that goes right into the battery, that will be one-half of your lithium-ion battery.”
If the abstract below piques your interest, you can read the full study in Applied Materials & Interfaces, a journal of the American Chemical Society.
Biomass can serve as a sustainable template for the synthesis of carbon materials but is limited by the intrinsic properties of the precursor organism. In this study we demonstrate that the properties of a fungal biotemplate can be tuned during cultivation, establishing a new electrode manufacturing process and ultimately improving the electrochemical performance of the biomass-derived electrode. More specifically, the carbon/nitrogen ratio of Neurospora crassa mycelia mats was shifted by 5-fold while generating cobalt nanoparticles into the hyphal structure originating from macroconidia spores. This shift was achieved through nitrate limitation and equal molar concentrations of Mg2+ and Co2+ in the growth media. The resulting mycelia mat was converted via a high-temperature pyrolysis process (800 °C) to produce a freestanding cobalt and nitrogen codoped electrode material with no postmodification. Ultimately, nitrogen doping resulted in one of the highest recorded specific reversible capacity for a freestanding biomass-derived lithium-ion anode (400 mAh g–1 at C/10). We observed an additional improvement in capacity to 425 mAh g–1 with the incorporation of 3 wt % Co. Our results show how shaping the chemical characteristics of an electrode during the growth of the biotemplate allows for sustainable carbon-based material manufacturing from a living (self-assembled) material.
[Image source: University of Colorado Boulder]

Ronnie Schreiber edits Cars In Depth, the original 3D car site.
More by Ronnie Schreiber
Latest Car Reviews
Read moreLatest Product Reviews
Read moreRecent Comments
- Probert They already have hybrids, but these won't ever be them as they are built on the modular E-GMP skateboard.
- Justin You guys still looking for that sportbak? I just saw one on the Facebook marketplace in Arizona
- 28-Cars-Later I cannot remember what happens now, but there are whiteblocks in this period which develop a "tick" like sound which indicates they are toast (maybe head gasket?). Ten or so years ago I looked at an '03 or '04 S60 (I forget why) and I brought my Volvo indy along to tell me if it was worth my time - it ticked and that's when I learned this. This XC90 is probably worth about $300 as it sits, not kidding, and it will cost you conservatively $2500 for an engine swap (all the ones I see on car-part.com have north of 130K miles starting at $1,100 and that's not including freight to a shop, shop labor, other internals to do such as timing belt while engine out etc).
- 28-Cars-Later Ford reported it lost $132,000 for each of its 10,000 electric vehicles sold in the first quarter of 2024, according to CNN. The sales were down 20 percent from the first quarter of 2023 and would “drag down earnings for the company overall.”The losses include “hundreds of millions being spent on research and development of the next generation of EVs for Ford. Those investments are years away from paying off.” [if they ever are recouped] Ford is the only major carmaker breaking out EV numbers by themselves. But other marques likely suffer similar losses. https://www.zerohedge.com/political/fords-120000-loss-vehicle-shows-california-ev-goals-are-impossible Given these facts, how did Tesla ever produce anything in volume let alone profit?
- AZFelix Let's forego all of this dilly-dallying with autonomous cars and cut right to the chase and the only real solution.

































Comments
Join the conversation
Betteridge's law of headlines confirmed.
Thinking outside the box.